링크 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/3176
문제 설명 :
N개의 도시와 그 도시를 연결하는 N-1개의 도로로 이루어진 도로 네트워크가 있다.
모든 도시의 쌍에는 그 도시를 연결하는 유일한 경로가 있고, 각 도로의 길이는 입력으로 주어진다.
총 K개의 도시 쌍이 주어진다. 이때, 두 도시를 연결하는 경로 상에서 가장 짧은 도로의 길이와 가장 긴 도로의 길이를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력 :
첫째 줄에 N이 주어진다. (2 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)
다음 N-1개 줄에는 도로를 나타내는 세 정수 A, B, C가 주어진다. A와 B사이에 길이가 C인 도로가 있다는 뜻이다. 도로의 길이는 1,000,000보다 작거나 같은 양의 정수이다.
다음 줄에는 K가 주어진다. (1 ≤ K ≤ 100,000)
다음 K개 줄에는 서로 다른 두 자연수 D와 E가 주어진다. D와 E를 연결하는 경로에서 가장 짧은 도로의 길이와 가장 긴 도로의 길이를 구해서 출력하면 된다.
출력 :
총 K개 줄에 D와 E를 연결하는 경로에서 가장 짧은 도로의 길이와 가장 긴 도로의 길이를 출력한다.
예제 입력 :
5
2 3 100
4 3 200
1 5 150
1 3 50
3
2 4
3 5
1 2
예제 출력 :
100 200
50 150
50 100
접근법 :
1) 어떻게 풀 것인가?
N이 10만 주어지고, 각 도시(정점) 쌍의 경로상에 존재하는 간선의 최솟값과 최댓값을 구해야한다.
먼저 완전탐색 기반으로 생각해보면,
특정 노드와 노드 사이에는 최대 N-1개의 도로가 존재할 수 있고,
이 경우 시간복잡도는 N(10만) * K(10만)으로 시간초과가 예상된다.
즉, 노드 사이의 경로를 압축해서 그 사이의 대표값을 기록하는 알고리즘이 필요하다.
트리에서 두 노드 간의 거리를 logN으로 줄여주는 대표적인 알고리즘은 LCA가 있다.
LCA에 대해서는 백준 11438 LCA 2 문제 먼저 추천 : https://subbak2.tistory.com/60
LCA의 logN 알고리즘을 구현할 수 있는 상태에서 문제에서 주어진 예제를 살펴보자.
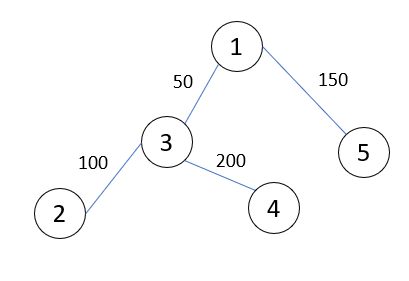
② 와 ⑤ 사이의 최솟값, 최댓값을 구한다고 가정을 하면,
먼저 최소공통조상을 구해야한다.
② - 최소공통조상 - ⑤ 가 도로 사이를 연결하는 경로이기 때문이다.
이 최소공통조상을 구하는 과정에서 각 경로 사이의 대표값을 저장한다면 최솟값, 최댓값을 쉽게 구할 수 있다.
parent[K][V] 를 정점 V의 2^K번째 조상 정점 번호
parent[K][V] = parent[K-1][parent[K-1][V]] 라는 점화식으로 최소공통조상을 구했다면,
minDist[K][V] 를 정점 V의 2^K번째 조상까지의 최소거리 도로
maxDist[K][V] 를 정점 V의 2^K번째 조상까지의 최대거리 도로 으로 만들어놓고
1) DFS 과정에서 cost를 갱신하고
// 아직 깊이를 모르면 → 미방문 노드
if (depth[next.target] == 0) {
dfs(next.target, cnt+1);
parent[0][next.target] = id; // 첫번째 부모를 기록
minDist[0][next.target] = next.cost; // 현재 cost로 갱신
maxDist[0][next.target] = next.cost; // 현재 cost로 갱신
}
2) fillParent를 하는 과정에서 minDist, maxDist를 갱신하고
// 부모 채우기
static void fillParent() {
for (int i = 1; i<=K; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j<=N; j++) {
// parent[K][V] = parent[K-1][parent[K-1][V]];
parent[i][j] = parent[i-1][parent[i-1][j]];
// 도로네트워크 추가
minDist[i][j] = Math.min( minDist[i-1][j], minDist[i-1][parent[i-1][j]]);
maxDist[i][j] = Math.max( maxDist[i-1][j], maxDist[i-1][parent[i-1][j]]);
}
}
}
3) LCA에서 minDist, maxDist를 추가로 갱신하면 된다.
// 최소공통조상
static void lca(int a, int b) {
// 1. depth[a] >= depth[b] 이도록 조정하기
if (depth[a] < depth[b]) {
int tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
max = -1;
// 2. 더 깊은 a를 2^K승 점프하여 depth를 맞추기
for (int i = K; i>=0; i--) {
if (Math.pow(2, i) <= depth[a] - depth[b]) {
min = Math.min(min, minDist[i][a]);
max = Math.max(max, maxDist[i][a]);
a = parent[i][a];
}
}
// 3. depth를 맞췄는데 같다면 종료
if (a == b) return;
// 4. a-b는 같은 depth이므로 2^K승 점프하며 공통부모 바로 아래까지 올리기
for (int i = K; i >= 0; i--) {
if (parent[i][a] != parent[i][b]) {
min = Math.min(min, Math.min(minDist[i][a], minDist[i][b]));
max = Math.max(max, Math.max(maxDist[i][a], maxDist[i][b]));
a = parent[i][a];
b = parent[i][b];
}
}
// 한 칸 위로 올라가서 공통부모 갱신
min = Math.min(min, Math.min(minDist[0][a], minDist[0][b]));
max = Math.max(max, Math.max(maxDist[0][a], maxDist[0][b]));
return;
}
자세한 내용은 코드 참고.
2) 시간복잡도
쿼리 횟수 M * 1번 연산시 시간 logN = O (M log N) 으로 문제를 통과하는데 무리는 없다.
(Java 기준 - 1,348ms)
3) 공간복잡도
N(10만)개의 Tree 이며, 인접리스트나 간선이 없으므로 고려하지 않음.
4) 풀면서 놓쳤던점
없음
5) 이 문제를 통해 얻어갈 것
① DFS 활용 (깊이 구하기)
② Tree 만들기
③ LCA 2^N 이용해 구현하기 + DP적 요소 활용
④ LCA 등 그래프 알고리즘에 최솟값, 최댓값 추가하기
Java 코드 :
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// 3176 도로 네트워크
public class Main {
static int N, K; // N : 정점수, K : 2의 지수
static int M; // M : 쿼리 수 (문제에서 K)
// LCA 관련 변수
static int[] depth;
static int[][] parent; // parent[K][V] 정점 V의 2^K번째 조상 정점 번호
// parent[K][V] = parent[K-1][parent[K-1][V]];
// TREE 변수
static ArrayList[] tree;
// 도로 네트워크 추가변수
static int[][] minDist; // minDist[K][V] 정점 V의 2^K번째 조상까지의 최소거리 도로
static int[][] maxDist; // maxDist[K][V] 정점 V의 2^K번째 조상까지의 최대거리 도로
static int min,max;
static class edge{
int target,cost;
public edge(int target, int cost) {
this.target = target;
this.cost = cost;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st;
// 1. 입력 & 변수 준비
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
// 2^K >= N인 첫번째 K 찾기, 문제조건 : N >= 2, K를 -1부터 시작해야 아래 값이 나옴
// N이 17이면 2^4 번째 조상까지 기록 필요 17 = 2^4 + 2^0
// N이 16이면 2^4 번째 조상까지 기록 필요 16 = 2^4
// N이 15이면 2^3 번째 조상까지 기록 필요 15 = 2^3 + 2^2 + 2^1 + 2^0
K = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i *= 2) {
K++;
}
// LCA 관련 변수 초기화
depth = new int[N + 1];
parent = new int[K + 1][N + 1]; // 2^K 까지 표현을 위해 K+1로 선언
// 도로 네트워크 변수 초기화
minDist = new int[K + 1][N + 1];
maxDist = new int[K + 1][N + 1];
// TREE 변수 초기화
tree = new ArrayList[N+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
tree[i] = new ArrayList<edge>();
}
int a,b,c;
for (int i = 1; i <= N-1; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 양방향 간선
tree[a].add(new edge(b, c));
tree[b].add(new edge(a, c));
}
// 2. DEPTH 확인
dfs(1, 1);
// 3. 2^N 까지 parent 채우기
fillParent();
// 4. LCA 진행
M = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i=1; i<=M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lca(a, b);
sb.append(min+" "+max+"\n");
}
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
// DEPTH 확인, 부모 기록 DFS
static void dfs(int id, int cnt) {
// 1. depth를 기록
depth[id] = cnt;
// 2. 자식들의 depth를 기록
int len = tree[id].size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
edge next = (edge) tree[id].get(i);
// 아직 깊이를 모르면 → 미방문 노드
if (depth[next.target] == 0) {
dfs(next.target, cnt+1);
parent[0][next.target] = id; // 첫번째 부모를 기록
minDist[0][next.target] = next.cost; // 현재 cost로 갱신
maxDist[0][next.target] = next.cost; // 현재 cost로 갱신
}
}
return;
}
// 부모 채우기
static void fillParent() {
for (int i = 1; i<=K; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j<=N; j++) {
// parent[K][V] = parent[K-1][parent[K-1][V]];
parent[i][j] = parent[i-1][parent[i-1][j]];
// 도로네트워크 추가
minDist[i][j] = Math.min( minDist[i-1][j], minDist[i-1][parent[i-1][j]]);
maxDist[i][j] = Math.max( maxDist[i-1][j], maxDist[i-1][parent[i-1][j]]);
}
}
}
// 최소공통조상
static void lca(int a, int b) {
// 1. depth[a] >= depth[b] 이도록 조정하기
if (depth[a] < depth[b]) {
int tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
max = -1;
// 2. 더 깊은 a를 2^K승 점프하여 depth를 맞추기
for (int i = K; i>=0; i--) {
if (Math.pow(2, i) <= depth[a] - depth[b]) {
min = Math.min(min, minDist[i][a]);
max = Math.max(max, maxDist[i][a]);
a = parent[i][a];
}
}
// 3. depth를 맞췄는데 같다면 종료
if (a == b) return;
// 4. a-b는 같은 depth이므로 2^K승 점프하며 공통부모 바로 아래까지 올리기
for (int i = K; i >= 0; i--) {
if (parent[i][a] != parent[i][b]) {
min = Math.min(min, Math.min(minDist[i][a], minDist[i][b]));
max = Math.max(max, Math.max(maxDist[i][a], maxDist[i][b]));
a = parent[i][a];
b = parent[i][b];
}
}
// 한 칸 위로 올라가서 공통부모 갱신
min = Math.min(min, Math.min(minDist[0][a], minDist[0][b]));
max = Math.max(max, Math.max(maxDist[0][a], maxDist[0][b]));
return;
}
}'알고리즘 Algorithm > BOJ 백준 (초급~중급)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ 백준] K번째 최단경로 찾기(1854) Java (0) | 2021.07.27 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ 백준] 단절선(11400) Java (0) | 2021.07.27 |
| [BOJ 백준] LCA 2(11438) Java (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| [BOJ 백준] 교수님은 기다리지 않는다(3830) Java (0) | 2021.07.26 |
| [BOJ 백준] 단절점(11266) Java (0) | 2021.07.25 |



