링크 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2580
2580번: 스도쿠
스도쿠는 18세기 스위스 수학자가 만든 '라틴 사각형'이랑 퍼즐에서 유래한 것으로 현재 많은 인기를 누리고 있다. 이 게임은 아래 그림과 같이 가로, 세로 각각 9개씩 총 81개의 작은 칸으로 이루
www.acmicpc.net
문제 설명 :
스도쿠는 18세기 스위스 수학자가 만든 '라틴 사각형'이랑 퍼즐에서 유래한 것으로 현재 많은 인기를 누리고 있다. 이 게임은 아래 그림과 같이 가로, 세로 각각 9개씩 총 81개의 작은 칸으로 이루어진 정사각형 판 위에서 이뤄지는데, 게임 시작 전 일부 칸에는 1부터 9까지의 숫자 중 하나가 쓰여 있다.
나머지 빈 칸을 채우는 방식은 다음과 같다.
- 각각의 가로줄과 세로줄에는 1부터 9까지의 숫자가 한 번씩만 나타나야 한다.
- 굵은 선으로 구분되어 있는 3x3 정사각형 안에도 1부터 9까지의 숫자가 한 번씩만 나타나야 한다.
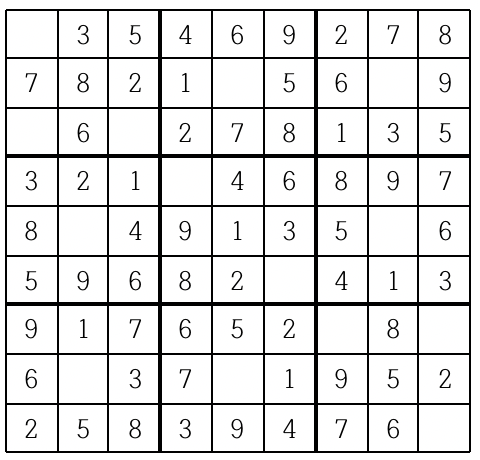
위의 예의 경우, 첫째 줄에는 1을 제외한 나머지 2부터 9까지의 숫자들이 이미 나타나 있으므로 첫째 줄 빈칸에는 1이 들어가야 한다.
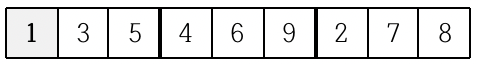
또한 위쪽 가운데 위치한 3x3 정사각형의 경우에는 3을 제외한 나머지 숫자들이 이미 쓰여있으므로 가운데 빈 칸에는 3이 들어가야 한다.

이와 같이 빈 칸을 차례로 채워 가면 다음과 같은 최종 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
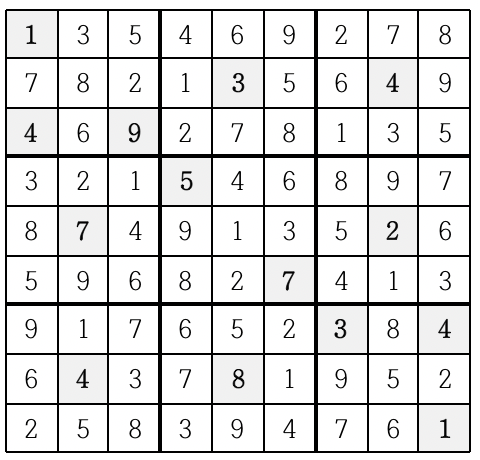
게임 시작 전 스도쿠 판에 쓰여 있는 숫자들의 정보가 주어질 때 모든 빈 칸이 채워진 최종 모습을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력 :
아홉 줄에 걸쳐 한 줄에 9개씩 게임 시작 전 스도쿠판 각 줄에 쓰여 있는 숫자가 한 칸씩 띄워서 차례로 주어진다. 스도쿠 판의 빈 칸의 경우에는 0이 주어진다. 스도쿠 판을 규칙대로 채울 수 없는 경우의 입력은 주어지지 않는다.
출력 :
모든 빈 칸이 채워진 스도쿠 판의 최종 모습을 아홉 줄에 걸쳐 한 줄에 9개씩 한 칸씩 띄워서 출력한다.
스도쿠 판을 채우는 방법이 여럿인 경우는 그 중 하나만을 출력한다.
예제 입력 :
0 3 5 4 6 9 2 7 8
7 8 2 1 0 5 6 0 9
0 6 0 2 7 8 1 3 5
3 2 1 0 4 6 8 9 7
8 0 4 9 1 3 5 0 6
5 9 6 8 2 0 4 1 3
9 1 7 6 5 2 0 8 0
6 0 3 7 0 1 9 5 2
2 5 8 3 9 4 7 6 0
예제 출력 :
1 3 5 4 6 9 2 7 8
7 8 2 1 3 5 6 4 9
4 6 9 2 7 8 1 3 5
3 2 1 5 4 6 8 9 7
8 7 4 9 1 3 5 2 6
5 9 6 8 2 7 4 1 3
9 1 7 6 5 2 3 8 4
6 4 3 7 8 1 9 5 2
2 5 8 3 9 4 7 6 1
접근법 :
1) 어떻게 풀 것인가?
2) 시간복잡도
3) 공간복잡도
4) 풀면서 놓쳤던점
5) 이 문제를 통해 얻어갈 것
Java 코드 :
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// 스도쿠 2580
public class Main {
static class location {
int y, x;
public location(int y, int x) {
this.y = y;
this.x = x;
}
}
static int[][] map = new int[10][10];
static boolean isComplete;
static int cnt;
static ArrayList<location> pointList;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 입력받는다
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
pointList = new ArrayList<location>();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (map[i][j] == 0) {
// 빈칸 좌표 저장
pointList.add(new location(i, j));
}
}
}
// 2. sudoku를 한다
sudoku(0);
// 3. 답을 출력한다 -- sudoku 중간에 바로 출력
// backtracking 방지를 위함
return;
}
static void sudoku(int cur) {
// 답이 하나라도 나왔으면 종료
if (isComplete)
return;
if (cur == pointList.size()) {
isComplete = true;
print();
return;
}
location curLoc = pointList.get(cur);
// 1부터 9까지 값 넣어보기
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// 1~9까지 값을 넣어보기
map[curLoc.y][curLoc.x] = i;
if (check(pointList.get(cur))) {
// 이 값을 넣어도 문제 없으니까 스도쿠 진행
sudoku(cur + 1);
}
}
map[curLoc.y][curLoc.x] = 0;
}
static boolean check(location point) {
// 1. 가로 쭉 확인 - first 값은 고정
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
// 자기 자신 pass
if (i == point.x)
continue;
// 이미 동일한 숫자가 나온 경우 불가(false)
if (map[point.y][point.x] == map[point.y][i]) {
return false;
}
}
// 2. 세로 쭉 확인 - second 값은 고정
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
// 자기 자신 pass
if (i == point.y)
continue;
// 이미 동일한 숫자가 나온 경우 불가(false)
if (map[point.y][point.x] == map[i][point.x]) {
return false;
}
}
// 3. 정사각형 확인
// 012 / 345 / 678
// 나누기 3 한다음에 보면 되겠다
int sy = point.y / 3;
sy *= 3;
int sx = point.x / 3;
sx *= 3;
for (int i = sy; i < sy + 3; i++) {
for (int j = sx; j < sx + 3; j++) {
// 자기 자신 pass
if (i == point.y && j == point.x)
continue;
// 이미 동일한 숫자가 나온 경우 불가 (false)
if (map[point.y][point.x] == map[i][j]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
static void print() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
sb.append(map[i][j]+" ");
}
sb.append("\n");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
C++ 코드 :
// 스도쿠 2580 C++
#if 1
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int map[10][10];
bool isComplete;
int cnt;
vector<pii> pointList;
void input();
void sudoku(int cur);
bool check(pii point);
void output();
int main() {
// 1. 입력받는다
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
input();
// 2. sudoku를 한다
sudoku(0);
// 3. 답을 출력한다 -- sudoku 중간에 바로 출력
// backtracking 방지를 위함
return 0;
}
void input() {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &map[i][j]);
if (map[i][j] == 0) {
// 빈칸 좌표 저장
pointList.push_back(pii(i, j));
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
void sudoku(int cur) {
// 답이 하나라도 나왔으면 종료
if (isComplete) return;
if (cur == cnt) {
isComplete = true;
output();
return;
}
// 1부터 9까지 값 넣어보기
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// 1~9까지 값을 넣어보기
map[pointList[cur].first][pointList[cur].second] = i;
if (check(pointList[cur])) {
// 이 값을 넣어도 문제 없으니까 스도쿠 진행
sudoku(cur + 1);
}
}
map[pointList[cur].first][pointList[cur].second] = 0;
}
bool check(pii point) {
// 1. 가로 쭉 확인 - first 값은 고정
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
// 자기 자신 pass
if (i == point.second) continue;
// 이미 동일한 숫자가 나온 경우 불가(false)
if ( map[point.first][point.second] == map[point.first][i]){
return false;
}
}
// 2. 세로 쭉 확인 - second 값은 고정
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
// 자기 자신 pass
if (i == point.first) continue;
// 이미 동일한 숫자가 나온 경우 불가(false)
if (map[point.first][point.second] == map[i][point.second]) {
return false;
}
}
// 3. 정사각형 확인
// 012 / 345 / 678
// 나누기 3 한다음에 보면 되겠다
int sy = point.first / 3;
sy *= 3;
int sx = point.second / 3;
sx *= 3;
for (int i = sy; i < sy + 3; i++) {
for (int j = sx; j < sx + 3; j++) {
// 자기 자신 pass
if (i == point.first && j == point.second) continue;
// 이미 동일한 숫자가 나온 경우 불가 (false)
if (map[point.first][point.second] == map[i][j]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
void output() {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++)
{
printf("%d ", map[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
#endif'알고리즘 Algorithm > BOJ 백준 (초급~중급)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ 백준] 치킨 배달(15686) C / C++, Java (0) | 2023.01.08 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ 백준] 단어 수학(1339) C++ (0) | 2023.01.08 |
| [BOJ 백준] 암호 만들기(1759) C++ (0) | 2023.01.08 |
| [BOJ 백준] N-Queen(9663) C++ (0) | 2023.01.08 |
| [BOJ 백준] 수찾기(1920) C++ (0) | 2023.01.08 |
